
Online customer service for after-sales problems
Contact now
Provide project content that meets your needs
Apply Now
Submit your message
Collaborate now
 E-Mail:
dawatertreatment@gmail.com
E-Mail:
dawatertreatment@gmail.com
Zero discharge, in terms of its content, on the one hand, is to control the discharge of waste generated in the production process and reduce it to zero; on the other hand, it is to make full use of the waste discharged as a last resort, and ultimately eliminate non-renewable resources and energy The presence. As far as the process is concerned, it refers to the transformation of wastes discharged in the production process of one industry into raw materials or fuels of another industry, so that relevant industries can form an industrial ecosystem through recycling. From a technical point of view, in the process of industrial production, the transformation of energy, energy and resources follows certain natural laws. It is impossible to achieve 100% conversion of resources into various energy, mutual transformation of various energies, and conversion of raw materials into products. transform. According to the law of conservation of energy and the law of immortality of matter, the lost part is finally discharged into the environment in the form of water, gas, sound, slag, and heat. my country's environmental protection work started relatively late. With the existing technical and economic conditions, it is even more difficult to truly reduce the waste discharged as a last resort to zero.
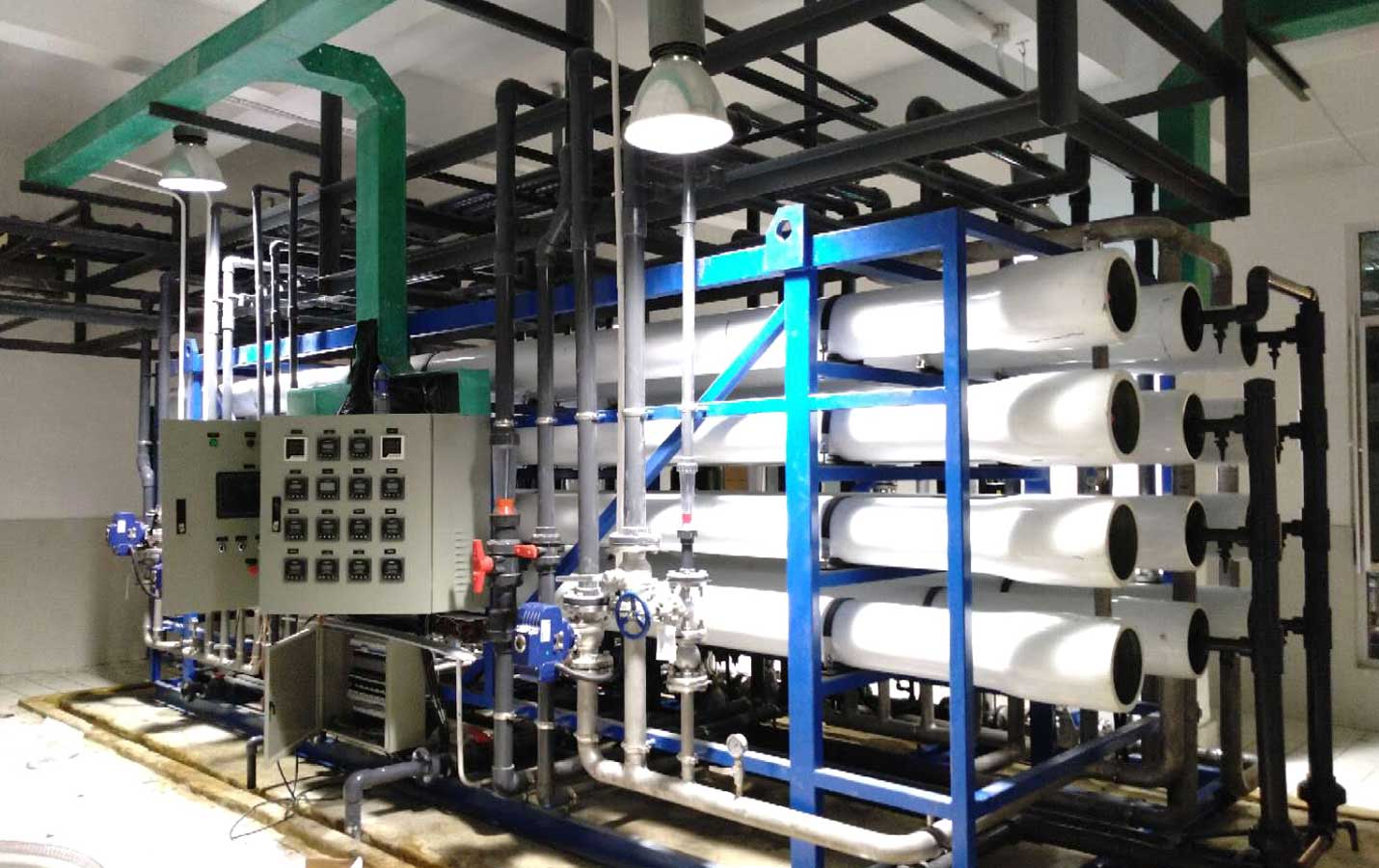

The zero-emission technology is a comprehensive application of physical, chemical and biochemical processes such as membrane separation, evaporative crystallization and drying to concentrate solid impurities in wastewater to a very high concentration. Most of the water has been recycled, leaving a small amount of water with solid waste. According to the specific situation of each enterprise, one of the following ways can be selected without discharging the system (this "zero emission" decision should at least consider the following three factors: environmental protection requirements - economic cost (enterprise competitiveness) - mdash ;Production safety).
1. Evaporation/Crystallization
2. Evaporation/Drying
3. Natural evaporation from solar evaporation ponds
4. Used to produce by-products, into solid products
5. Spray into the incinerator for garbage disposal
6. Absorbed by solid waste (such as fly ash) and treated as solid waste