Online customer service for after-sales problems
Contact now
Provide project content that meets your needs
Apply Now
Submit your message
Collaborate now
 E-Mail:
dawatertreatment@gmail.com
E-Mail:
dawatertreatment@gmail.com
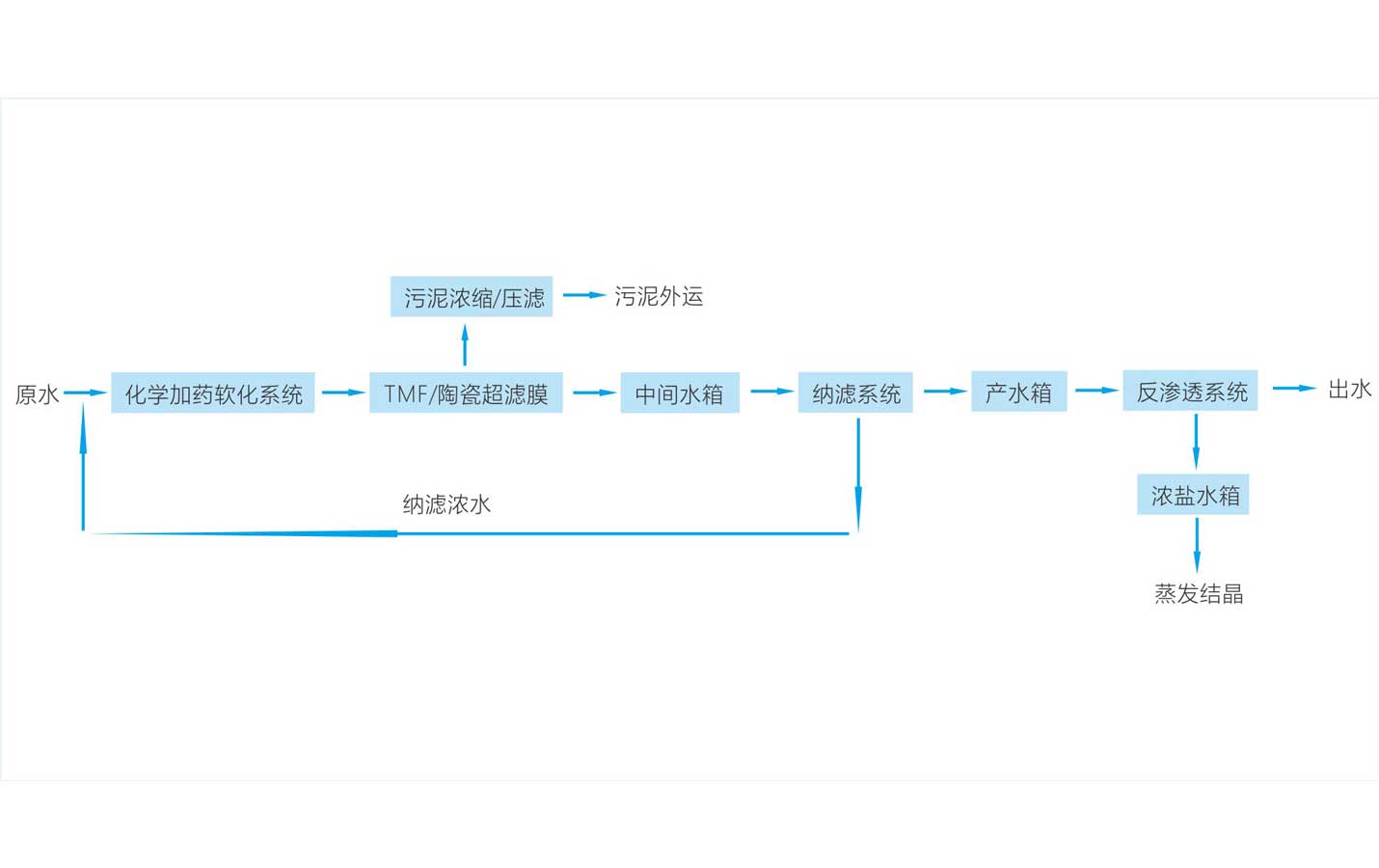
Nanofiltration (NF) is used to separate substances with relatively small molecular weights, such as inorganic salts or small molecular organics such as glucose and sucrose, from solvents. Nanofiltration, also known as low-pressure reverse osmosis, is an emerging field of membrane separation technology. Its separation performance is between reverse osmosis and ultrafiltration, allowing some inorganic salts and some solvents to pass through the membrane to achieve separation.
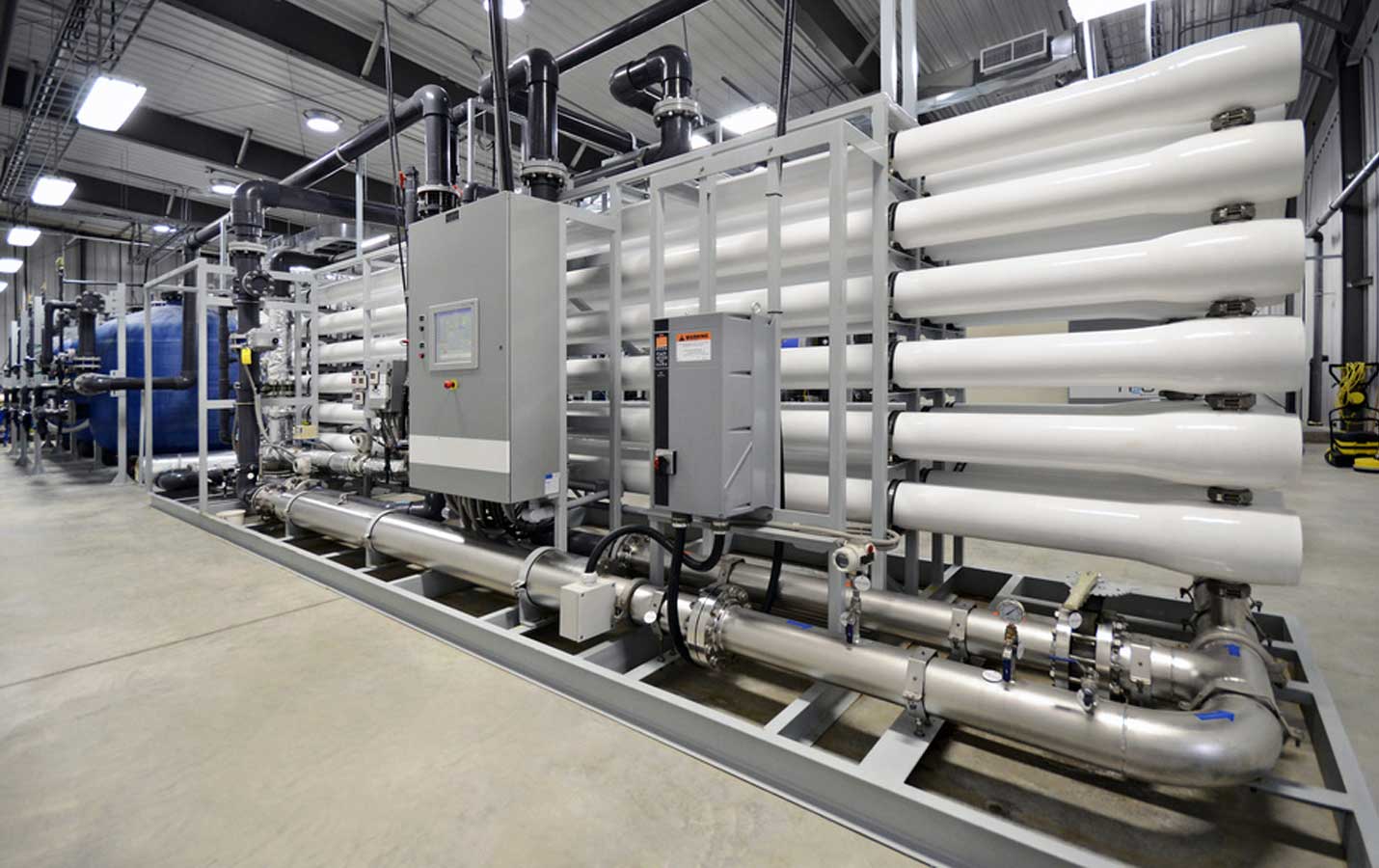

Nanofiltration membranes are charged membranes that can perform electrical adsorption. Under the same water quality and environment, the pressure required by the nanofiltration membrane is less than the pressure required by the reverse osmosis membrane. Therefore, in terms of separation principle, nanofiltration and reverse osmosis have similar aspects and different aspects. The pore size and surface characteristics of the nanofiltration membrane determine its unique performance, and it has different Donann potentials for ions of different charges and valences; the separation mechanism of the nanofiltration membrane is the coexistence of sieving and dissolution and diffusion, and also has charge repulsion. It can effectively remove divalent and multivalent ions, remove various substances with molecular weight greater than 200, and partially remove monovalent ions and substances with molecular weight less than 200; the separation performance of nanofiltration membranes is significantly better than ultrafiltration and microfiltration. Compared with the reverse osmosis membrane, it has the advantages of partial removal of monovalent ions, low process osmotic pressure, low operating pressure, and energy saving.