Iron and manganese removal water treatment system
DAWT·2022-05-09
Introduction
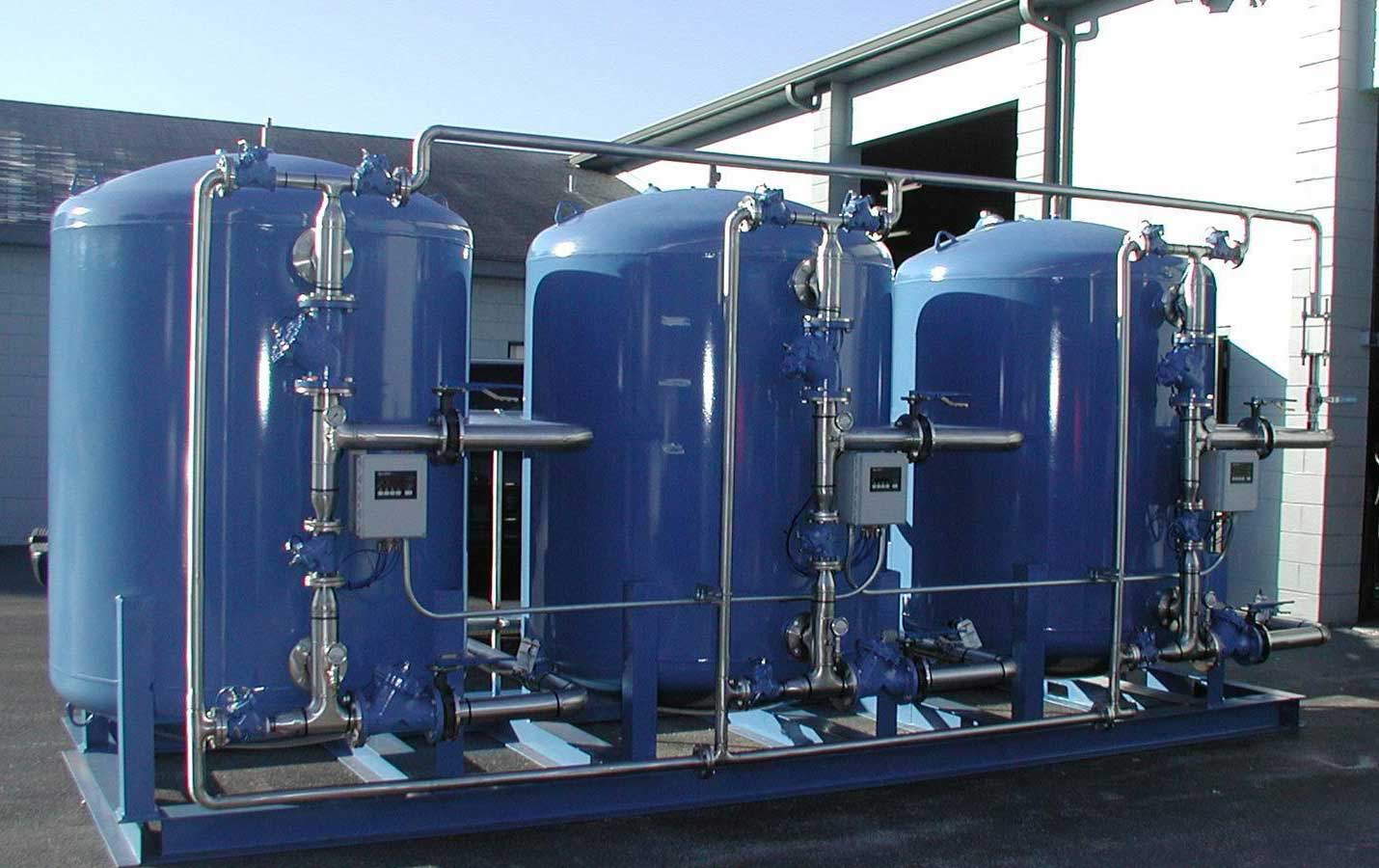
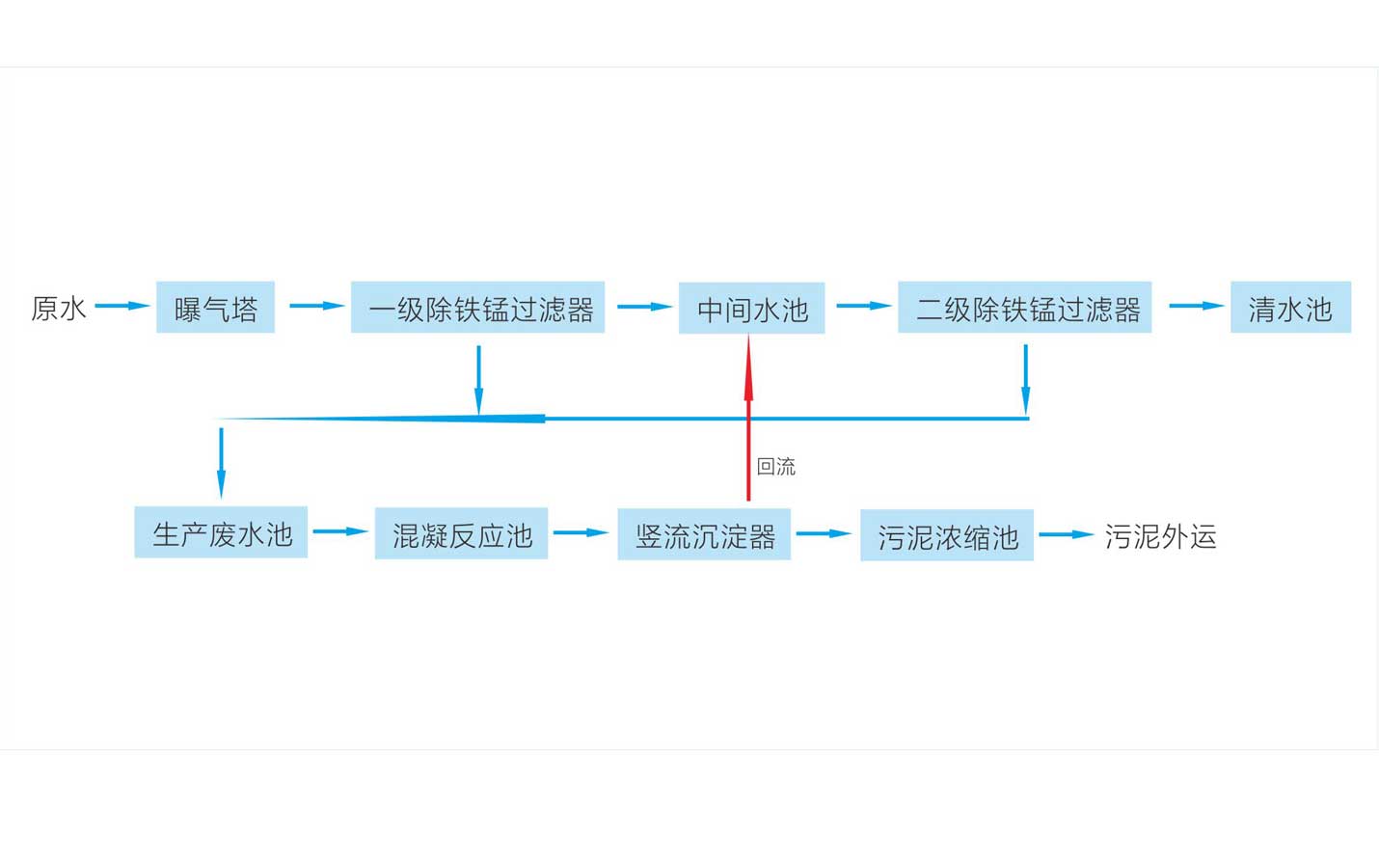
The iron and manganese removal device is composed of a main body, an ejection aeration device, an intermediate booster pump, a recoil pump, a control system, a water supply pump and a pipe network system.
This equipment adopts the latest international technology "active biofilm contact oxidation method" to remove iron and manganese from groundwater. After the iron and manganese-containing sewage is aerated, the iron ions in the water begin to oxidize. When the water flows through the manganese sand and the filter layer, due to the chemical action of the filter material and the iron (manganese) bacteria on the surface of the filter The biochemical effects of iron chiridi, unicellular iron bacteria, and Trichoderma rust, etc.). Biochemical melon begins to occur in the filter material layer, and the contact oxidation reaction and physical retention and adsorption can greatly accelerate the oxidation, fixation and removal of iron and manganese in water. Especially in the process of treating micro-polluted iron and manganese-containing groundwater, iron (manganese) bacteria can not only effectively remove iron and manganese, but also use ammonia nitrogen in water as a nutrient source for reproductive replacement. The effect of iron removal and removal of ammonia nitrogen. The iron content in the treated water is less than 0.3MG/L and the manganese content is less than 0.1MG/L.
The iron and manganese removal equipment is mainly composed of: filter equipment, piping, KTG oxygenation equipment, water pump, water tank, etc. The processing subject is a filtering device. The iron and manganese removal device is widely used in mineral water, pure water pretreatment to remove iron and manganese precipitation, as well as iron and manganese removal in geothermal engineering and swimming pool engineering, domestic water, textile industry water, and paper industry water.

Working principle
The working principle of the iron and manganese removal device: use the oxidation method to oxidize the low-valent iron ions and low-valent manganese ions in the water into high-valent iron ions and high-valent manganese ions, and then remove them by adsorption and filtration to reduce the iron and manganese content in the water. The filter material adopts refined quartz sand and refined manganese sand. The main component of refined manganese sand is manganese dioxide (MnO2), which is a good catalyst for the oxidation of ferrous iron to ferric iron. The content of MnO2 in the refined manganese sand is very high, and its iron removal effect is very ideal. The pH value of the groundwater containing iron and manganese is greater than 5.5, and the Fe2+ can be oxidized to Fe3+ in contact with the refined manganese sand. In addition to the catalytic effect, there is also a layer of iron filter film gradually formed on the surface of the refined manganese sand filter material as an active filter film during filtration, so that it can play a catalytic role. The active filter membrane is composed of R-type ferric hydride R-FeO(OH), which can carry out ion exchange reaction with Fe2+ and replace the equivalent hydrogen ions.
Process flow


 E-Mail:
dawatertreatment@gmail.com
E-Mail:
dawatertreatment@gmail.com

